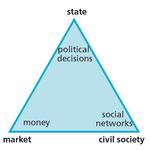
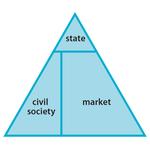
- 1.1: The three main areas of social science
- 1.2: Gender roles are determined by the social environment
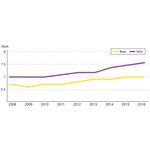
- 1.3: Father's share of parental leave days as a percentage in the Nordic countries
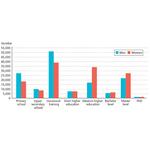
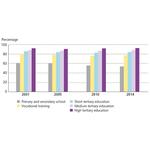
- 1.4: The population's highest completed education, calculated for men and women, 15-69 years
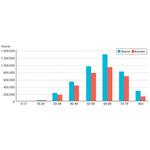
- 1.5: Average pension savings by age, 2015
- 1.6: The two main policy approaches to gender roles and gender equality in Denmark
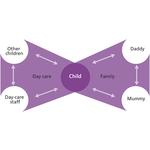
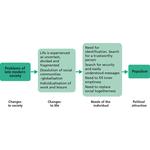
- 2.2: The butterfly model (dual socialisation)
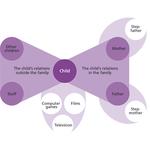
- 2.4: Four different family types (emphasis on individuality and/or community)
- 2.5: Multi-socialisation model
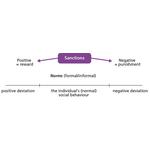
- 2.6: Social control - regulation of social behaviour through norms and sanctions
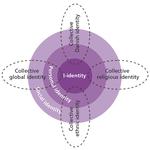
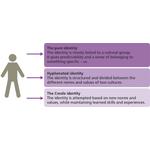
- 2.8: The four levels of identity
- 2.9: The development of role-taking - from the significant to the generalised
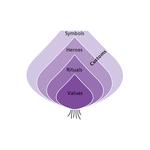
- 2.12: Hofstede's onion model of the elements of a culture
- 2.14: Impact of culture on immigrants' and descendants' choice of identity
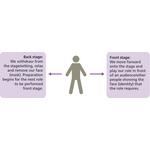
- 2.17: Face, front stage and back stage - the identity is constantly at play
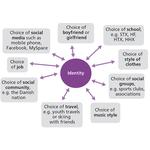
- 2.19: The choice of roles is significant for our identity
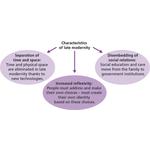
- 3.3: Anthony Giddens' three key characteristics of late modernity
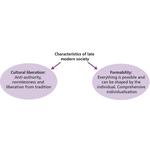
- 3.4: Thomas Ziehe's characteristics of late modernity
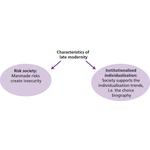
- 3.6: Ulrich Beck's characteristics of late modern society
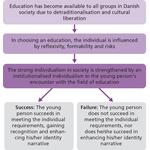
- 3.8: Education plays a significant role in the identity narrative of young people
- 3.9: Young Danes who feel anxious, afraid or depressed
- 3.10: Differences in marks between girls and boys in the Danish upper secondary school
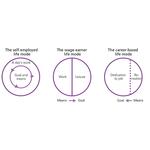
- 4.1: Three different life modes
- 4.2: Minerva model
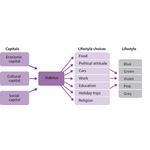
- 4.4: The structure of Pierre Bourdieu's concepts
- 4.8: Like father, like son - or? Bar chart of the proportion of 25-year-olds with completed youth education by the parents' highest education
- 4.9: Income development in Denmark in the period 2000-2015, index constant prices
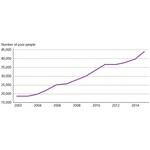
- 4.11: Trends in the number of economically poor people in Denmark, 2002-2015
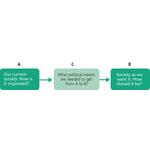
- 5.1: Three components of a political ideology
- 5.2: The function of the political ideologies in different periods
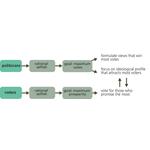
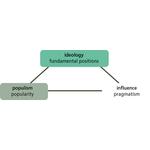
- 5.3: Citizens' attraction to populism in late modern society
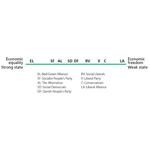
- 5.4: Danish political parties from left to right based on redistribution policy
- 5.5: Parties according to old and new politics
- 5.6: Downs' Model
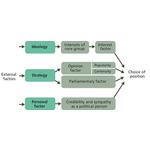
- 5.7: Molin's Model
- 5.8: The behaviour triangle
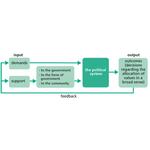
- 6.1: Easton's model of the political system
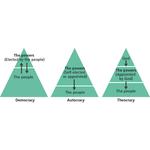
- 6.2: Three political forms of government
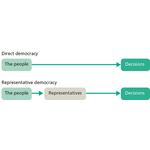
- 6.3: Two forms of democracy
- 6.5: The normative chain of governance - this is how it should look
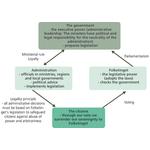
- 6.6: The parliamentary chain of governance - a more realistic version
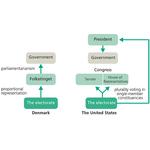
- 6.7: Two political systems: Denmark and the United States
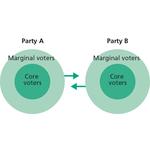
- 6.8: Core voters and marginal voters
- 6.9: Importance of the electoral system for the election result
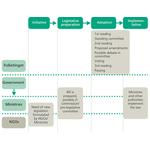
- 6.12: Denmark's legislative process
- 6.13: The mutual means of control of Folketinget and the government
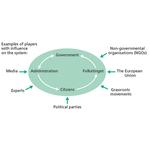
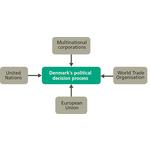
- 6.15: Political decision processes in Denmark are influenced by the world around us
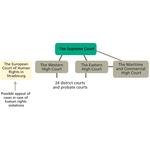
- 6.17: The organisation of the Danish legal system
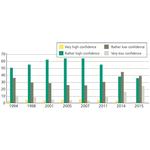
- 6.23: The declining confidence of the Danish population in the elected politicians. Percentages of the population
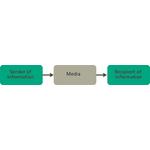
- 7.1: Basic model for mediated communication
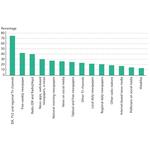
- 7.2: Citizens' use of media to be updated on news and topical issues. Percentage of the population over 14 years
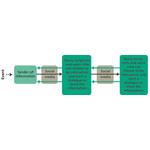
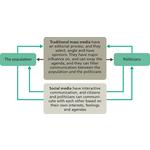
- 7.3: Model for news coverage by traditional mass media
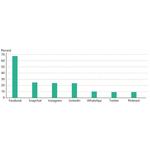
- 7.5: Danes on the social media in percent of the population between the age of 16 and 89, 2016
- 7.6: Model for communication on the social media
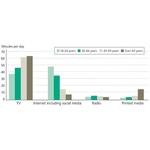
- 7.7: Average time consumption of Danes over the age of 17
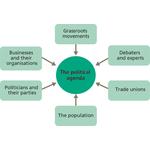
- 7.8: The model for the battle of the political agenda
- 7.10: Communication between citizens and politicians in different media
- 7.11: To which extent do you agree or disagree, that the tone of a debate on Facebook keeps you from participating?
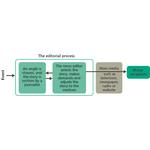
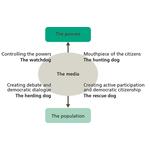
- 7.12: The role of the media in our democracy
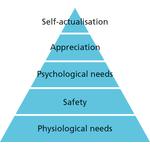
- 8.1: Abraham Maslow's hierarchy of needs
- 8.2: The OECD's index for life satisfaction
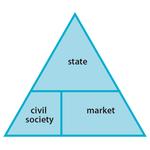
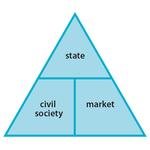
- 8.3: The welfare triangle
- 8.4: Supply, demand and price - examples of the market mechanism
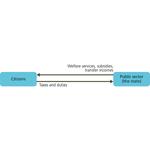
- 8.6: Relationship between citizen and state
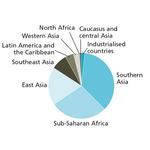
- 8.7: Number of hungry people in the world by region
- 8.8: GDP development in Denmark, 2010 prices (1966-2016)
- 8.10: Denmark's exports and imports in DKK billion (2000-2016)
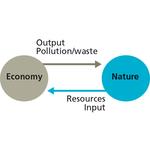
- 8.11: Economy and nature
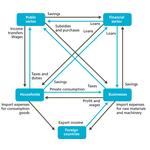
- 8.12: The economic circuit
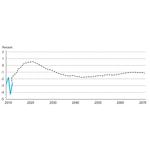
- 8.13: The economy goes up and down
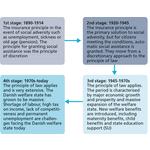
- 9.1: Four stages in the development of the Danish welfare state
- 9.2: Total taxation by tax, type, percentages
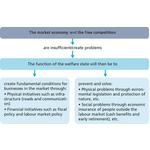
- 9.3: The functions of the welfare state
- 9.4: The universal welfare model
- 9.5: The residual welfare model
- 9.6: The corporative welfare model
- 9.8: Internal and external challenges putting pressure on the Danish welfare state model
- 9.9: The government's budget deficit. Percentage of GDP
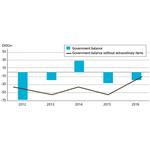
- 9.10: The general government balance, 2012-2016
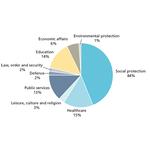
- 9.11: Public expenditure by sector, 2016. Percentage
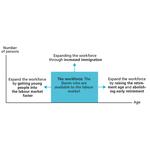
- 9.12: Ways of expanding the workforce
- 9.15: The "gain" at undeclared work compared with declared work